When you see a high white blood cell count, it’s usually your body’s way of saying it’s fighting off an infection. But that’s not the whole story for your long-term health. The cause could also be stress, inflammation, certain medications, or even an underlying disease. Think of it as your body's internal alarm system going off—a signal that, if persistent, could impact your longevity.
The Quick Answer to High White Blood Cell Counts
Getting to grips with what causes a high white blood cell count is the first real step towards understanding and optimising your long-term health. A high count, which doctors call leukocytosis, isn’t a condition in itself. Instead, it’s a crucial clue—a biomarker telling you that something is up inside your body. It could be a temporary physical stressor or a sign of chronic inflammation that could affect your healthspan.
To get an accurate picture, your doctor will likely order a Full Blood Count (FBC). This is a standard blood test that provides a clear snapshot of your immune system's activity. If you want to dive deeper into what all the numbers mean, our guide to understanding the full blood count explained can shed more light on the subject.
This infographic gives a great visual comparison between a normal and an elevated white blood cell count, highlighting infection as a common cause.
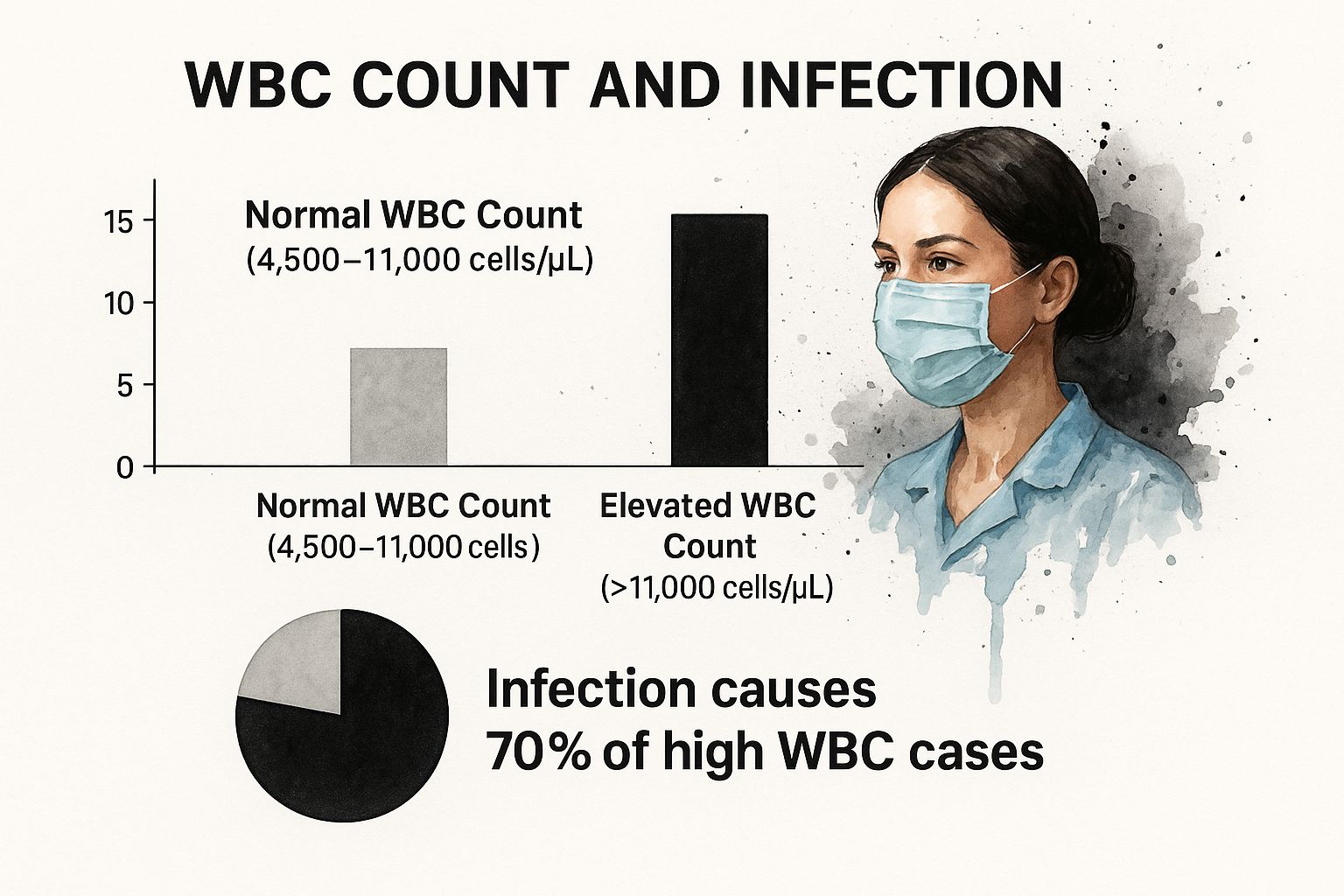
As a general rule, a count that tips over 11,000 cells per microlitre (µL) is considered high. The data clearly shows that infections are responsible for roughly 70% of these cases.
Decoding the Primary Triggers
While infections are the most common culprit, understanding the other triggers is essential for a proactive approach to longevity. For example, chronic inflammation can keep your count consistently high, which is a key risk factor for age-related diseases. Managing this is a cornerstone of a long and healthy life.
To make sense of it all, let’s look at the main triggers in more detail.
Primary Causes of Elevated White Blood Cells
This table breaks down the most common reasons for a high white blood cell count, explaining how each one works and giving some real-world examples.
| Cause | Mechanism | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Infections | The body kicks white blood cell production into high gear to track down and eliminate invaders like bacteria, viruses, or fungi. | Pneumonia, urinary tract infections (UTIs), the flu, or appendicitis. |
| Inflammation | Autoimmune or chronic inflammatory conditions put the immune system on constant high alert, leading to a steady stream of white blood cells. | Rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or even a severe allergic reaction. |
| Medications | Some drugs, especially corticosteroids, can directly signal the bone marrow to release more white blood cells into circulation. | Prednisone, lithium, or certain types of asthma inhalers. |
| Physical Stress | Your body can react to intense physical or emotional strain by releasing a surge of white blood cells. This spike is usually temporary. | Running a marathon, recovering from major surgery, or going through a period of extreme anxiety. |
As you can see, a high count can be triggered by a wide range of factors. That's why context and tracking your levels over time are crucial for turning this data into actionable health insights.
Understanding Your Immune System's First Responders
Before diving into what causes high white blood cell counts, it's worth appreciating what these cells do. Think of your white blood cells (WBCs), also called leukocytes, as your body's personal security detail, constantly on patrol to keep you safe. They originate deep inside your bone marrow, poised and ready to be deployed at the first sign of trouble.
When your body senses a threat—whether it's a virus, nasty bacteria, or even tissue damage from an injury—it sounds the alarm. In a flash, your bone marrow kicks into high gear, pumping out these specialised cells and releasing them into your bloodstream. This rapid response is precisely what you want from a healthy, resilient immune system.
The Different Types of Immune Responders
Not all white blood cells are created equal. Just like an emergency needs different specialists, your body deploys various WBCs to handle specific threats. Knowing these roles is key to understanding what a high count might be telling you about your long-term health.
Here’s a look at the main players on your immune team:
- Neutrophils: These are the most abundant and act as the immediate front-line soldiers. They swarm to the site of an infection or injury to engulf invaders.
- Lymphocytes: This group includes B-cells and T-cells. They are the intelligence agents, creating antibodies to remember and fight off pathogens you've encountered before.
- Monocytes: Think of these as the "cleanup crew." They arrive after the initial battle to clear away dead cells and debris, a vital part of healing and taming inflammation.
- Eosinophils and Basophils: These are specialised cells that primarily jump into action during allergic reactions and parasitic infections.
This image gives you a microscopic peek at what these different white blood cells look like.
You can see how each cell's unique structure is perfectly suited to its specific job in defending your body.
Why This Foundation Matters for Longevity
So, why does this matter for your long-term health? A temporary spike in your WBC count is normal; it shows your immune system is working correctly. The concern for longevity arises when that count stays high, suggesting a state of chronic inflammation or a persistent immune response that can accelerate aging and wear down your body over time.
A healthy immune system knows when to fight and when to stand down. It’s this ability to return to balance that's crucial for longevity. Chronic activation, flagged by consistently high WBC counts, is a major focus in longevity science because it can fuel many age-related diseases.
While it’s important to understand the causes behind a high white blood cell count, it's more empowering to know how to support a balanced immune system. This includes lifestyle choices and sometimes exploring natural supplements for immune system support. By understanding what a normal immune response looks like, you’re better equipped to spot trends and take action to protect your future health.
How Infections and Inflammation Trigger a WBC Surge
Think of your body as a well-guarded castle. When invaders like bacteria or viruses get past the gates, your immune system sounds the alarm, ordering your bone marrow to send out a massive wave of white blood cells. This is one of the most common reasons for a high white blood cell count.
This biological call to arms is your first line of defence. The newly dispatched WBCs, especially a type called neutrophils, race through your bloodstream to the site of the attack. Their job is simple but crucial: find and destroy the invaders before they can do real damage. This process is incredibly effective, but it’s the long-term state of your immune system that truly impacts your longevity.
The Link Between Acute Infection and WBC Levels
The connection is direct: the more invaders, the more defenders your body needs. A simple infection can cause your WBC count to double or triple in hours. This spike is a completely normal and healthy response.
This rapid increase is only temporary. As soon as the infection is controlled, your body gives the 'all clear' signal, and your WBC count gradually settles back to baseline. It’s a beautiful example of your immune system’s ability to respond and adapt—a key component of a healthy, long life.
When Inflammation Becomes the Problem for Longevity
While a short-term infection causes a temporary surge, chronic inflammation tells a different, more concerning story for your long-term health. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or persistent low-grade inflammation can trick your body into keeping its immune system on high alert all the time.
In this state of constant readiness, the bone marrow continually produces more white blood cells than necessary. This sustained elevation, known as chronic leukocytosis, contributes to long-term tissue damage and is a recognised risk factor for many age-related diseases. From a longevity perspective, it's like leaving an engine running in the red zone indefinitely—it causes wear and tear.
It’s a bit like a fire alarm that just won't turn off. Over time, this constant state of alert can exhaust your immune system and create an environment that promotes cellular aging.
That’s why tracking your WBC count over the long term can offer powerful clues about hidden inflammatory processes. Looking at which specific types of cells are elevated provides even more detail. For a deeper dive into this, have a look at our article explaining what it means when your neutrophils are high and lymphocytes are low.
How Your Medicines Can Affect Your White Blood Cell Count
It’s easy to assume that a high white blood cell count points straight to an infection or inflammation, but sometimes the cause is sitting right there in your medicine cabinet. Quite a few common medications can directly influence your bone marrow, telling it to produce more white blood cells or changing how they circulate in your bloodstream.
This can cause a temporary spike in your lab results. Knowing this is crucial for accurate health tracking. It helps you and your doctor distinguish between a medication side effect and a genuine health signal that requires action for your long-term well-being.
Common Drugs That Can Raise WBC Counts
One of the best-known examples is a group of drugs called corticosteroids – think prednisone. These are powerful anti-inflammatory medicines that can trigger the bone marrow to release a flood of neutrophils into the blood. It’s like a fire alarm going off for a drill; the cells are mobilised, but there's no actual threat to fight.
Several other medications can also push your WBC levels up:
- Lithium, a common treatment for certain mental health conditions.
- Beta-agonists, the active ingredients in many asthma inhalers.
- Granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSF), which are powerful drugs given specifically to boost WBC production, often for patients undergoing cancer therapy.
It's so important to have this context. Without knowing about these medication effects, a high WBC count might be mistaken for a sign of infection, leading to unnecessary tests or anxiety. This is why providing a full list of your medications is non-negotiable for getting an accurate picture of your health.
The good news is that this effect is usually temporary and reverses once the medication is stopped. It’s a physiological response, not a disease process in itself.
The Complicated Case of Cancer Treatments
Things get more complex with treatments like chemotherapy. Chemotherapy works by targeting fast-dividing cells, which unfortunately includes our own immune cells, often leading to a sharp drop in the WBC count right after a treatment.
But here’s where it gets interesting. In the recovery period between chemo cycles, the bone marrow often kicks into high gear, working overtime to replenish its defensive army.
This can create a massive "rebound" effect, where the WBC count shoots up well above the normal range before it eventually levels out. This pattern is a normal part of the treatment journey. In fact, it's a positive sign that the immune system is resilient and fighting to rebuild itself—a crucial step toward long-term health and recovery.
Connecting High WBC Counts to Cancer and Chronic Disease
It’s one thing for your white blood cell count to spike when you’re fighting off a cold, but it’s another entirely when it stays high for no obvious reason. This persistent elevation can be a subtle but critical signal, often pointing to chronic, low-grade inflammation. From a longevity standpoint, this simmering state of alert can create an internal environment where more serious health conditions, including certain cancers and chronic diseases, are more likely to develop.
This is why viewing your WBC count as a long-term trend, rather than a single snapshot, is a powerful strategy for longevity. Think of chronic inflammation as your immune system being stuck in ‘on’ mode. This constant activation can, over years, contribute to cellular damage and disrupt normal bodily functions, laying the groundwork for problems down the road.
Unpacking the Link to Cancer
The connection between long-term inflammation and cancer is a major focus in medical research. A consistently high WBC count suggests your body's inflammatory processes are in overdrive, and this environment can, unfortunately, help cancer cells grow and survive. On top of that, some cancers—particularly blood and bone marrow cancers like leukaemia—directly cause the body to churn out huge numbers of abnormal white blood cells.
The research paints a pretty clear picture. A landmark UK Biobank study looked at over 424,000 adults and found a striking link. People whose total white blood cell counts were in the highest quartile had a 67% greater risk of developing lung cancer than those in the lowest quartile. This really underscores how chronic inflammation can be a powerful driver of cancer, even for people who have never smoked.
Actionable Longevity Insights
Knowing this gives you the power to be proactive about your health. By keeping an eye on your WBC count over time, you gain a valuable window into your body’s internal inflammatory state. If you notice your levels are consistently high without a clear reason, like a recent infection, it’s a clear sign to dig a little deeper with your doctor.
So, how can you turn this knowledge into practical health strategies?
- Adopt an Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle: This is your first line of defence. Focus on a diet packed with colourful fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Things like regular exercise and finding healthy ways to manage stress are also proven to help cool down systemic inflammation.
- Track Your Trends, Not Just a Single Result: A single blood test is just one moment in time. What really matters is the pattern. Is your WBC count slowly creeping up over several tests? That’s a trend worth discussing with your healthcare provider.
- Have an Informed Conversation: Use your WBC data as a starting point for a conversation with your doctor. Catching chronic inflammation early opens the door to interventions that can significantly lower your long-term risk of developing serious diseases.
Your white blood cell count is far more than just a number on a lab report. When you start to see it as a key indicator of your long-term health, it becomes a powerful catalyst for making smarter choices that support a longer, healthier life.
Linking Elevated WBCs to Cardiovascular Risk
For decades, we’ve been told to watch our cholesterol and blood pressure to protect our hearts. While those are still vital, another piece of the puzzle is emerging as a powerful predictor of cardiovascular health: your white blood cell count. A persistently high WBC count, driven by chronic inflammation, can be a quiet signal that your arteries are in trouble.
Think of it this way: your blood vessels should be smooth, clear motorways for blood to flow freely. Chronic inflammation, however, turns these motorways into a permanent construction zone. This inflammation, often flagged by a high level of neutrophils, can damage the delicate inner lining of your arteries, making them sticky and more likely to build up plaque.
Inflammation as a Heart Health Predictor
This low-grade, simmering inflammation creates a hazardous environment inside your blood vessels. The immune cells involved, particularly neutrophils, can release enzymes and reactive oxygen species that make existing plaques unstable. An unstable plaque is far more dangerous because it can rupture, leading to a blood clot that could block blood flow and trigger a heart attack or stroke.
This isn't just a theory; it's backed by solid research. Studies using UK Biobank data have shown that high neutrophil counts are strongly linked to an increased risk of death from cardiovascular events. This tells us that the inflammation these cells create is a key player in making plaques volatile, which can have fatal consequences. You can read the full research on neutrophil-mediated inflammation to see the science for yourself.
Your WBC count, especially the neutrophil level, can be seen as an early warning system for your cardiovascular system. It offers a glimpse into the inflammatory activity that may be silently damaging your arteries long before traditional symptoms appear.
Actionable Steps for Longevity
Understanding this link gives you a powerful tool for your longevity strategy. Keeping an eye on your WBC differential adds a crucial layer of insight that goes beyond a standard cholesterol test. If you notice a trend of rising neutrophils, it's a prompt to discuss proactive strategies with your doctor.
Here’s how you can turn this knowledge into action:
- Focus on an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Load up on foods rich in omega-3s (like salmon and walnuts), antioxidants (found in berries and leafy greens), and fibre to help manage inflammation naturally.
- Prioritise Stress Management: Chronic stress fuels inflammation. Practices like mindfulness, regular exercise, and getting enough sleep are non-negotiable for cooling down your body's inflammatory response.
- Integrate Advanced Testing: A simple WBC count is a great start, but pairing it with other inflammatory markers gives you a much clearer picture. To get a better sense of what this involves, check out our guide on why blood tests for heart disease are essential.
By looking at your WBC count through the lens of cardiovascular risk, you can take meaningful steps to protect your heart and support a longer, healthier life.
Your Questions About High WBC Counts, Answered
Getting blood test results back can be a little unnerving, especially when you see a number flagged as 'high'. Let's break down what a high white blood cell count really means, so you can understand what's happening inside your body and how it relates to your long-term health goals.
A high count isn't always a sign of trouble, but it's your body's way of telling you something is going on.
What Counts as a 'High' WBC Count?
For most adults, a healthy white blood cell count sits somewhere between 4,500 and 11,000 cells per microlitre (µL) of blood. If your results come back higher than 11,000 cells/µL, it's generally considered elevated. This condition is known as leukocytosis.
It's worth noting that the exact 'normal' range can differ slightly from one lab to another. Your doctor will always interpret your results based on the specific reference range provided by their lab.
Can Stress Really Raise My White Blood Cell Count?
Absolutely. Think of it as your body's built-in alarm system. When you're under intense physical or emotional pressure—whether from a gruelling workout, recovering from surgery, or even a bout of severe anxiety—your body goes into "fight or flight" mode.
This triggers the release of stress hormones, which in turn can signal your bone marrow to push more white blood cells out into your bloodstream. They’re like first responders getting ready for a potential emergency.
This kind of spike is usually temporary. Once the stress eases up and your body calms down, your WBC count should settle back into its normal range. From a longevity perspective, it's the numbers that stay high without a clear reason that warrant further investigation as a sign of chronic stress or inflammation.
When Should I Be Worried?
Seeing a high WBC count when you’re already fighting off a known bacterial infection is completely normal; it’s a sign your immune system is doing its job. The time to be proactive and book a follow-up with your doctor is when things are less clear-cut.
You should seek advice if:
- Your count is very high, but you don't have any obvious signs of an infection.
- The number stays elevated over several blood tests taken weeks or months apart.
- You’re also dealing with other persistent symptoms, like unexplained weight loss, constant tiredness, fevers, or drenching night sweats.
These situations could point to an underlying issue, like a chronic inflammatory condition, that needs a closer look to safeguard your health down the line.
At Lola, we believe that understanding your health shouldn't be complicated. Our at-home and in-clinic blood tests give you detailed, doctor-reviewed insights, making it easy to track your body's signals over time. Take control of your health journey and find out more at https://lolahealth.com.
